
Hanoi 2021 report brings essential information about all aspects of the city, include Society, Economy, Operational environment, Economic development.

In 2020, Hanoi contributed about 17% of the country's total budget revenue, catching up with Ho Chi Minh City's budget revenue. Although the economic situation in Vietnam faced many complex and unpredictable changes, including natural disasters and the COVID-19 epidemic, the GDP in Vietnam reached more than 271 billion US Dollars in the same year, with the GDP growth slowed down to 2.9% in 2020, the one was at 7% in 2019. Hanoi 2021 report from Statista brings us essential information about all aspects of the city, including Society, Economy, Operational environment, and economic development.
Hanoi ranked 134th out of 200 Global Business Cities, while Ho Chi Minh City ranked 145th. Hanoi's global business cities index was 38.87, while the top 1 of Tokyo index was 100 and 2nd ranked London was 99.25. Ho Chi Minh city's global business cities index was 35.47, lower than the one in Hanoi.

According to the United Nations forecast, Hanoi's total population in 2020 was 4.68 million, with a growth rate of nearly 36%. In reality, according to the population census, the total population of Hanoi in April 2019 was 8.1 million people. With this result, Hanoi is the second-most populous city in Vietnam, only after Ho Chi Minh City (8,9 million people). The cost of living in Hanoi was estimated at 27.480 USD.
Noi Bai International Airport (HAN) is the largest international airport in the North of Vietnam, 30km away from the city center with up to 15 connections. Other airports include Hai Phong, Thanh Hoa, and Van Don.
With a society score of 12.43, Hanoi ranked 83rd out of 200 global business cities in the Society Subindex. The first ranks belong to Calgary city in Canada with the society score at 20; the following is London at 19.80.
According to the United Nations forecast, the population of Hanoi city is growing faster than an average city in this region. Hanoi's total population in 2020 was 4.7 million people and is predicted to increase 36% to reach 6.4 million people in 2030. In Southeast Asia, the total population in 2020 was 7.5 million people and predicted to increase 20.7% to reach 9 million people in 2030.
According to Globaldatalab 2020, Statista 2020, the inhabitants in Hanoi have 2.4 years less education than in the high regional performer. The English proficiency in Hanoi is low, with the score at 481, higher when compared to the country score at 473. The English proficiency score can indicate a city's competitive advantages and global citizen status. The top 1 countries worldwide belong to the Netherlands with an English Proficiency Index of 652, and the top 1 city worldwide is Copenhagen (Denmark), with a Proficiency Index of 659.
The cost of living in the Hanoi capital was lower than in this region in general. Through the Statista report, the cost of living in Hanoi was 27,480 US$ in 2019, lower than in Southeast Asia (at 30,795 US$). The Gini coefficient expresses the degree of inequality in income distribution between classes of residents in Hanoi was 0.34 in 2019, lower than in Southeast Asia (0.40). The unemployment rate in Hanoi in 2016 at 6.7% is 1.7 higher than in Southeast Asia (3.95%).

Hanoi residents have the highest life expectancy in the country (over 75 years old), while the average life expectancy of people in Vietnam is only 73.4. According to World Bank 2019 and Statista 2019, Hanoi's life expectancy was 74.9 years old, ranking 149 among 100 country-level data. In the same report, Ho Chi Minh City ranked 135, with the life expectancy was 75.8 years old.
The safety index is between 1 and -1; the higher values in this index indicate higher levels of safety. This index is calculated from various elements (including the homicide rates, the estimated risk of kidnapping, the security risk, the political risk). The safety index of Hanoi is 0.6, which is considered unsafer than the average for this region, and higher than the one in Ho Chi Minh City.

The Economy SubIndex is calculated based on these elements: GDP per capita, Unemployment, Corruption Control, Rent in the City Center, and Rent in the Suburb. The economy score of Hanoi is 16.02, ranked 173rd out of 200 global business cities in the Economy Subindex. The highest economy index was at 35, belonging to San Francisco, according to the Statista 2020 research.
The city GDP per capita of Hanoi was at US$5,038, being US$73,725 behind regional high-performer Singapore. The GDP per capita in Ho Chi Minh city is 4,931 US$, lower than the Hanoi capital in the same year.
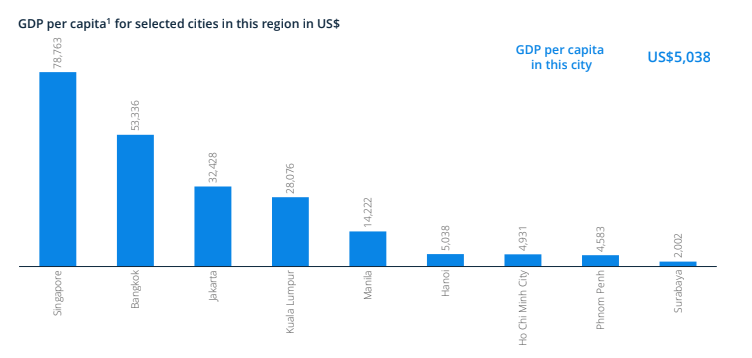
Due to the smaller population, Hanoi's GDP per capita is lower than the regional average. The business environment in Hanoi city shows a positive when the number of days to start a business is about 16 days, lower than the regional average of 34.9 days. The international hotel brands are not well represented in Hanoi, while the international restaurant chains have a strong presence. Some hotel brands that are in the Hanoi capital such as Hilton, Mercure, and Hyatt. The international restaurant chains include Starbuck, Macdonal, KFC, Subway, Domino Pizza, Pizza Hut, Dunkin, etc.
The average monthly rent in Hanoi is at 747US$ (about 17 million VND) for a 3 room apartment in the city center, lower than the highest for this region. The monthly rent in Hanoi is US$475 behind regional high-performer Ho Chi Minh city.
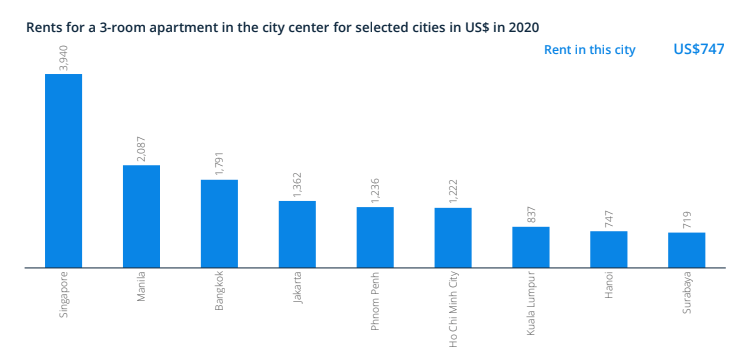
While the average monthly rent for a 3 room apartment outside Hanoi city is US$487, it was US$1,249 lower than Phnom Penh, the city that has the highest monthly rents in the region.
The Real Estate Index value shows the stability, affordability, and level of taxation of the city's property market. This index in Hanoi city is higher than the regional average, slightly lower than Ho Chi Minh city.

The Operational Environment Subindex of Hanoi capital was 14.56, ranked 119th out of 200 Global Business Cities in the highest range at 35 belong to Tokyo (Japan). Top 10 Asian cities in Global Business Cities Index: Operational Environment including Tokyo (Japan), Hong Kong, Seoul & Incheon (Korea), Beijing & Shanghai (China).
The internet penetration in Hanoi is higher than the regional average, according to the Statista Digital Market Outlook 2020. In 2020, Hanoi showed a smartphone penetration rate of 75.6%, lower than the regional average (76.6%), and the internet penetration rate at 75.7%, higher than the regional average (70.8%).

Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh city are both locations that have a stock exchange in Vietnam 2020.
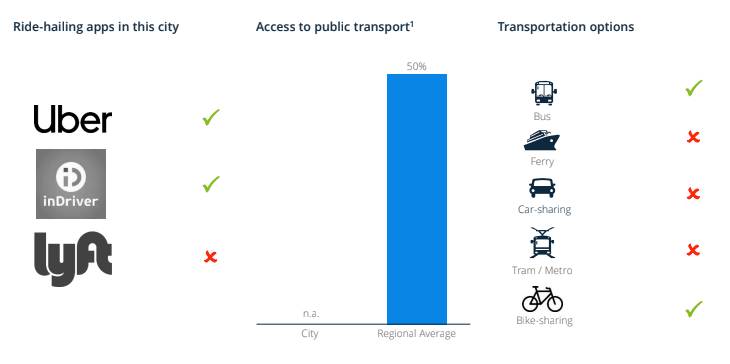
About the transport, Uber and inDriver are ride-hailing apps used in Hanoi in 2020. Besides ride-hailing apps, the resident can choose other transportation options, including bus and bike-sharing. There is zero population with access to public transport in percent, according to the UN-Habitat & Statista report 2020.
The air passengers in 2019 in Hanoi at 29 million people were lower than the regional average. The air freight was about 700kt and is 57.75 kt compared to the regional average, showing the country's positive in building and development.
Covid Impact on Air Freight in Vietnam
The recent outbreak of the pandemic, especially during the peak period close to Tet 2021 and the middle of 2021, made the revenue of the aviation industry decrease by about 80% compared to the same period in 2020.
Vietnamese airlines are still maintaining the combination of cargo transportation on passenger aircraft. So, due to 5 Airlines operating simultaneously, specialized freight is still a gap in Vietnam's aviation industry because there is no single airline operating exclusively in freight transport.
Vietnam has less than 1 doctor and 2 nurses for every 1,000 people.
The Digital Health Report in Vietnam published on January 20 records that as of 2018, Vietnam had 77,995 doctors and 128,386 nurses nationwide. This is a lower number compared to the total population of the country, which is less than 1 doctor and 2 nurses/1,000 people. In Hanoi, there are 0.83 physicians per 1,000 inhabitants.
The number of universities in Hanoi was lower than the regional average. There were 11 universities in Hanoi in 2019, behind the 4.2 regional averages of the universities. Hanoi had 21 international schools in 2020, lower than the regional averages of the international schools (47.1).
Hanoi ranked 146th out of 200 Global Business Cities in the Charisma Subindex with a score of 2.99. Tokyo (Japan) has the highest Charisma subindex, and Seoul (Korea) is an Asian city in the top 10 Charisma subindex.
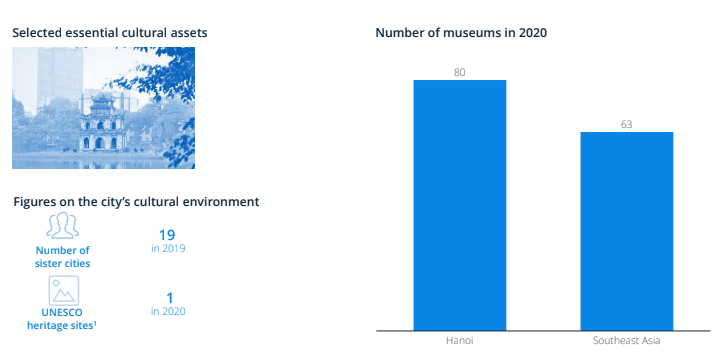
Although owning more museums than the regional average and a large number of embassies or consulates in this city, Hanoi capital was less famous on Instagram than other cities in this region. This was supposedly due to the air pollution concentration; Hanoi's air pollution concentration of 102 μg/m3 was 410% higher than the WHO guideline.
In Vietnam, Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi capital ranked in the global cities with average connectivity globally despite the economic size and connectivity being still lower compared to other cities in Southeast Asia. Finally, the Statista report gives us an overview of the Hanoi capital, but not profoundly about the economy and the global integration. Download the full report to get complete data.